1. Introduction - Why Falco + Nginx Plugin is Needed
Web Application Security Reality
Modern web applications are constantly exposed to serious security threats such as:
- SQL Injection: Unauthorized database access
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Malicious script execution in user browsers
- Directory Traversal: Unauthorized access to system files
- Command Injection: Arbitrary command execution on servers
Solutions Provided by Falco + Nginx Plugin
falco-plugin-nginx is a plugin that adds Nginx access log analysis functionality to Falco, a CNCF project. This enables real-time detection of attack patterns such as SQL injection, XSS, directory traversal, and command injection from requests passing through Nginx.
Key Features:
🔍 Real-time Attack Detection
Instantly analyzes Nginx access logs to discover attacks like SQLi and XSS
⚡ Ultra-lightweight Operation
Minimal overhead with Go language implementation
📝 Flexible Rule Creation
Define and customize attack patterns flexibly in YAML format
2. System Architecture & Operating Principles
Overall Architecture
📊 System Architecture Flow
/var/log/nginx/access.log
Real-time Analysis
nginx_rules.yaml
Log Output
Detailed Operating Principles
📥 Step 1: Log File Monitoring
falco-plugin-nginx operates as part of the Falco framework, monitoring the Nginx access log file (/var/log/nginx/access.log) in real-time like tail -f. Every time a new log entry is added, reading and parsing are executed immediately.
🔍 Step 2: Log Analysis and Pattern Extraction
The following elements are extracted and analyzed from each log entry:
- IP Address: Identification of request source
- HTTP Method: Determination of GET/POST etc.
- Request Path: Inspection of target URL
- Query Parameters: Primary area where attack patterns lurk
- User-Agent: Identification of attack tools
- Response Status: Determination of attack success/failure
🎯 Step 3: Threat Determination by Rule Engine
The extracted information is matched against predefined YAML-based rule sets (nginx_rules.yaml). This rule engine performs the following processing:
- Pattern Matching: Attack detection through regex and string patterns
- Severity Determination: Classification into Critical/Warning/Notice/Info levels
- Context Analysis: Evaluation of IP address, path, and parameter combinations
- Whitelist Processing: Exclusion of legitimate traffic
🚨 Step 4: Alert Generation and Output
When threats are detected, structured alerts are generated:
- Detection Logs: Detailed information with timestamps
- Attack Classification: Categories like SQLi/XSS/CMDi etc.
- Source Information: IP address, User-Agent etc.
- Attack Content: Actual payload and detection reason
Target Attack Pattern Examples
| Attack Type | Severity | Detection Target | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| SQL Injection | Critical | Query Parameters | ' OR '1'='1 |
| XSS | Warning | Script Tags | <script>alert(1)</script> |
| Directory Traversal | Critical | Path Traversal | ../../etc/passwd |
| Command Injection | Critical | Command Execution | ;cat /etc/passwd |
3. Environment Setup - AWS EC2 Setup
Recommended Environment Specifications
Recommended specifications for building an effective test environment:
| Item | Recommended Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Instance Type | t2.micro or higher | Works within free tier |
| OS | Ubuntu 22.04 LTS | Long-term support version |
| Kernel | 5.8 or higher | Modern eBPF support |
| Memory | 1GB or more | Minimum required for Falco operation |
| Storage | 10GB or more | For log file storage (if needed) |
4. Installation - Easy One-liner Setup
🚀 One-liner Installation
The easiest method is to use the official installation script:
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/takaosgb3/falco-plugin-nginx/main/install.sh | sudo bash📋 Installation with Test Environment
To simultaneously set up sample sites for attack testing:
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/takaosgb3/falco-plugin-nginx/main/install.sh \ | sudo SETUP_TEST_CONTENT=yes bash💡 Processes Executed by Installation Script
- Dependency resolution (jq, Nginx configuration check)
- Falco installation (modern eBPF mode enabled)
- falco-plugin-nginx binary placement
- Detection rule file configuration
- Falco configuration update
- Service startup and enablement
⚠️ Installation Notes
If permission errors or kernel version issues occur, check system updates and Falco dependencies. Also ensure to test functionality in the test environment after installation.
5. Test Environment Setup
Installation Startup Screen
When installation starts properly, the following screen will be displayed:
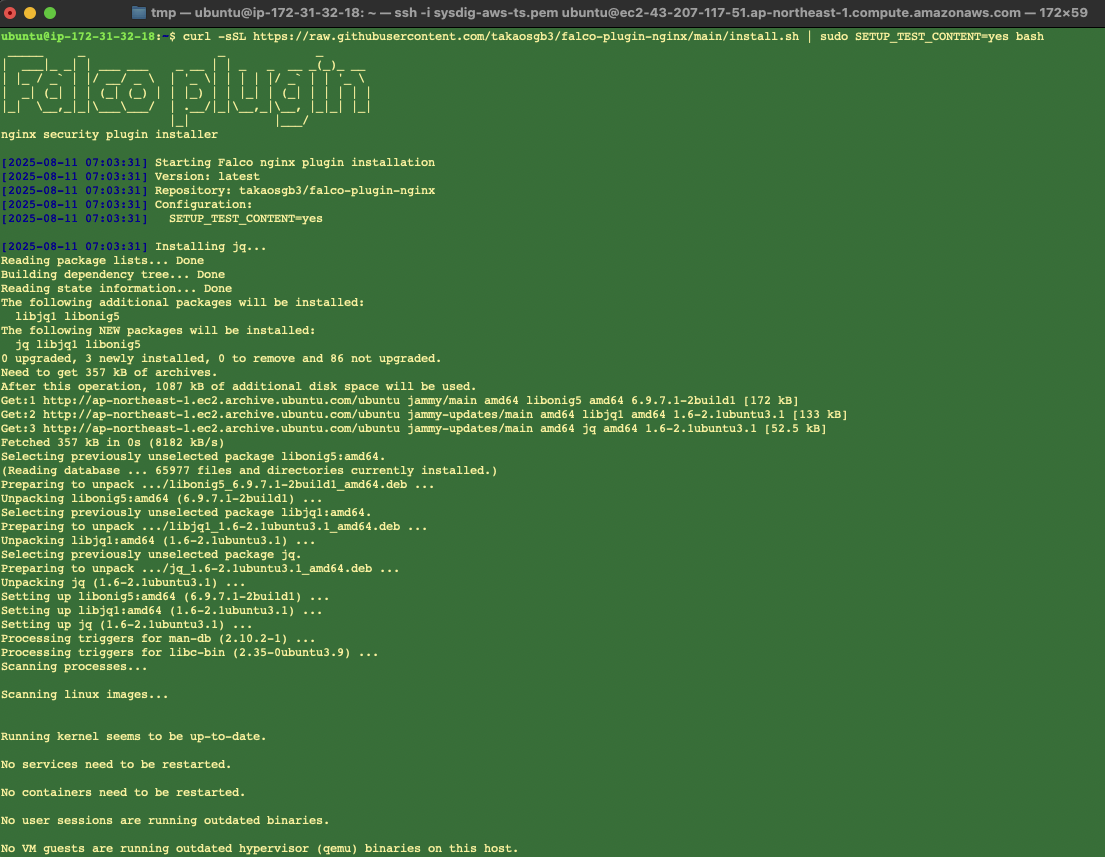
falco-plugin-nginx installation startup screen
Test Environment Setup
When installed with the SETUP_TEST_CONTENT=yes option, a sample site for attack testing is automatically built:
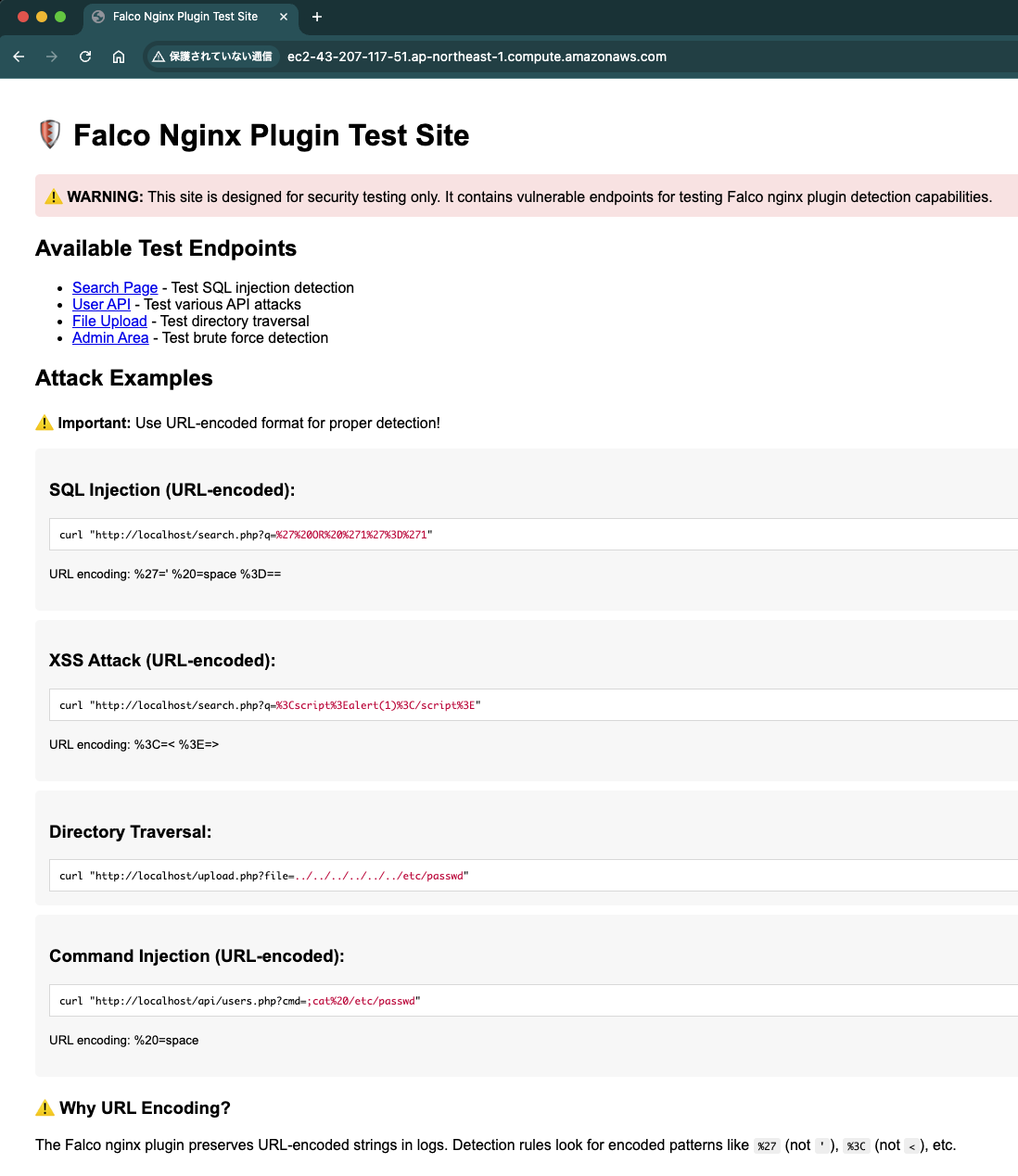
Security testing dedicated site - provides test endpoints for various attack patterns
Installation Completion and Test Preparation
When installation is complete, test methods are provided as the next step:
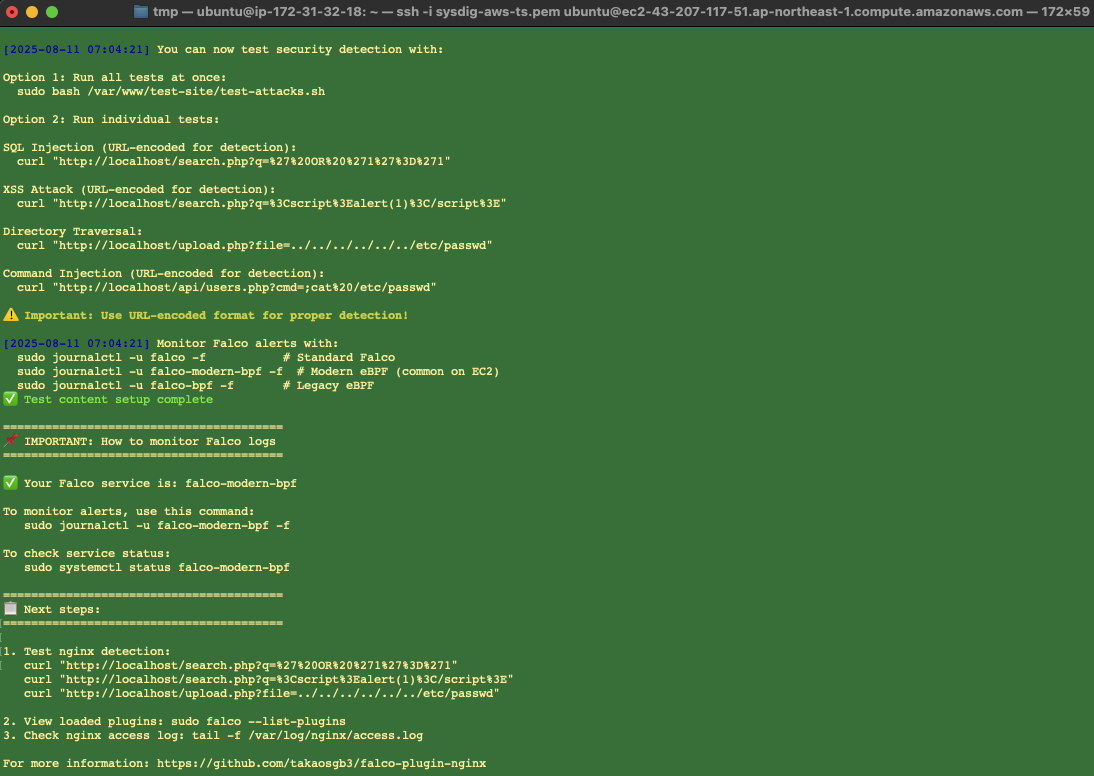
Post-installation test method guidance - displays test commands for various attack patterns and Falco log monitoring methods
💡 Test Environment Features
- Dedicated Test Pages: Dedicated endpoints for each attack pattern
- URL Encoding Support: Testing in the same format as actual attacks
- Detection Confirmation Function: Real-time Falco alert verification
- Safe Environment: Isolated test-dedicated environment
6. Attack Pattern Verification
Starting Real-time Monitoring
First, monitor Falco logs in real-time in a separate terminal:
sudo journalctl -u falco-modern-bpf -f -o catExecuting Attack Tests
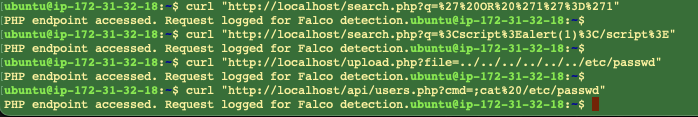
Actual attack test execution and real-time detection
1. SQL Injection Attack
curl "http://localhost/search.php?q=%27%20OR%20%271%27%3D%271"After URL decoding: ' OR '1'='1
This attack attempts to bypass authentication by making the logical condition of the SQL statement always true.
Critical [NGINX SQLi] ip=127.0.0.1 method=GET path=/search.php qs=q=%27%20OR%20%271%27%3D%271 ua=curl/7.81.0 status=2002. XSS Attack
curl "http://localhost/search.php?q=%3Cscript%3Ealert(1)%3C/script%3E"After URL decoding: <script>alert(1)</script>
This is an attack that attempts to inject malicious JavaScript code into web pages.
Warning [NGINX XSS] ip=127.0.0.1 method=GET path=/search.php qs=q=%3Cscript%3Ealert(1)%3C/script%3E ua=curl/7.81.0 status=200Confirming Detection Results
You can confirm that all executed attack patterns have been detected:

Detection logs of various attack patterns by Falco
7. Custom Rule Creation
Understanding Rule Structure
Falco rules consist of three elements:
1. list
Define values and patterns for detection targets
2. macro
Define condition combinations in a reusable form
3. rule
Define actual detection conditions and output
Custom Rule Creation Example
Detecting Unauthorized Access to Admin Pages
# List of admin paths
- list: admin_paths
items: ["/admin", "/administrator", "/wp-admin", "/phpmyadmin"]
# List of allowed admin IPs
- list: admin_ips
items: ["192.168.1.100", "10.0.1.50"]
# Macro to determine Nginx events
- macro: is_nginx_event
condition: (evt.source = nginx)
# Rule to detect unauthorized admin access
- rule: NGINX Unauthorized Admin Access
desc: Detect unauthorized access to admin pages
condition: >
is_nginx_event and
(nginx.path startswith "/admin" or nginx.path in (admin_paths)) and
not (nginx.ip in (admin_ips))
output: >
[UNAUTHORIZED ADMIN ACCESS] Suspicious admin access detected
(ip=%nginx.ip method=%nginx.method path=%nginx.path ua="%nginx.ua"
status=%nginx.status size=%nginx.size)
priority: Critical
tags: [nginx, web, unauthorized, admin]Rule Validation and Deployment
1. Syntax Check
sudo falco --validate /etc/falco/rules.d/local_nginx_rules.yaml2. Rule Application
sudo systemctl restart falco-modern-bpf3. Operation Verification
curl "http://localhost/admin/" -H "User-Agent: testbot"8. Conclusion
What We Achieved
✅ Environment Setup
Built Falco + Nginx plugin operating environment on AWS EC2
✅ Attack Detection
Demonstrated detection of SQLi, XSS, Directory Traversal, and Command Injection
✅ Rule Understanding
Acquired detection logic and customization methods
Security Improvement Effects
- Enhanced Visibility: Real-time detection of previously invisible attack patterns
- Rapid Response: Minimized time lag from attack occurrence to detection
- Cost Efficiency: High-function security monitoring with open source
- Integration: Easy integration with existing monitoring and alert infrastructure